A metric is an expression which describes a computation that will be performed over the project's data. Metrics are written in a custom query language, which is fairly simple and doesn't require users to know SQL. A metric written in this language is then translated to SQL by a backend service and executed as multidimensional query on data warehouse.
...
| Key | Type | Optionality | Description | Constraints | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
id | string |
| choose a custom string identifier for the query property | (a-z0-9_-) | ||||||||
type | string |
| dwh query property, dwh query function, or a number |
| ||||||||
value | string long decimal |
| string identifier of a dataset property, which the function will be applied to (for string with variable name (for long or decimal value (for |
|
content.options
| Key | Type | Optionality | Description | Constraints | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
aggregateBy | array |
| specifies datasets which the metric will be aggregated to if specified, always | [null] | ||||||||
acceptAggregateBy | array |
| specifies datasets which the metric is allowed to be aggregated to array of dataset names, or name prefixes (with the
|
| ||||||||
dontAggregateBy | array |
| specifies datasets which the metric is not allowed to be aggregated to array of dataset names, or name prefixes (with the
|
| ||||||||
withoutFilters | array |
| specifies dataset properties not to be explicitly joined into the final query array of dataset properties
|
| ||||||||
acceptFilters | array |
| specifies dataset properties to be explicitly joined into the final query array of dataset properties
|
| ||||||||
filterBy | object |
| object specifying the filter of the metric | |||||||||
places | integer |
| the number of places to round the metric result to
|
...
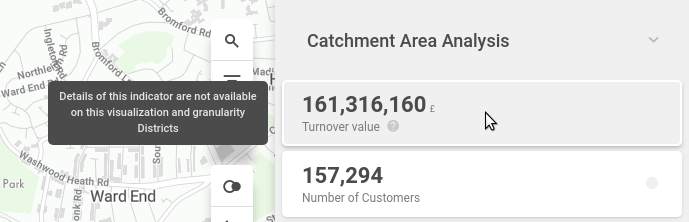
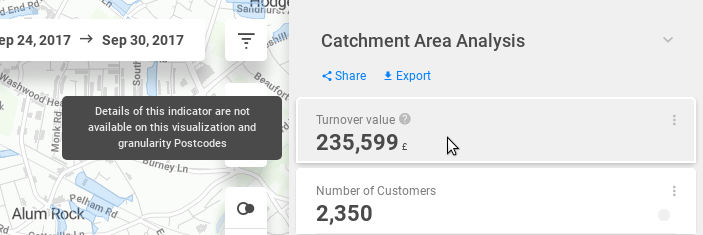
Using these options, the indicator card will show an explanation of why is there no metric result.
_
withoutFilters has 3 use cases:
...
Window functions provide the ability to perform calculations across sets of rows that are related to the current query row.
| Identifier | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| integer ranging from 1 to the argument value, dividing the partition as equally as possible |
|
function_rank | rank of the current row with gaps |
|
function_percentile | value below which a given percentage of observations in a group of observations fall |
input values sorted = (105.9, 75.2, 61.1, 42.7, 35.2, 21, 10)
|
function_row_number | a unique number for each row starting with 1. For rows that have duplicate values, numbers are arbitrary assigned. |
|
...
function_plus,function_minusandfunction_multiplyaccept 2 or more argumentsfunction_divideandfunction_moduloaccept exactly 2 arguments
| Identifier | Example |
|---|---|
|
|
function_minus |
|
function_multiply |
|
function_divide | 7 / 2 = 3.5 |
function_modulo | 7 mod 2 = 1 |
...
| Identifier | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
function_round | a rounding function (round to specific number of places) | function_round(56.157094235, 1) = 56.2 |
Conditional functions
| Identifier | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| defines the default value to use if the result of aggregate function is null |
|
...
| Identifier | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
eq | is equal |
|
ne | negated |
|
in | in range |
|
lt | lower than |
|
lte | lower than or equal |
|
gt | greater than |
|
gte | greater than or equal |
|
isNull | is null |
|
isNotNull | is not null |
|
inAttribute | is in attribute | see the usage in a complete metric example above |
notInAttribute | is not in attribute | complementary to the inAttribute example |
...